Osteochondrosis is the most severe form of spinal degenerative disease and is based on damage to the intervertebral disc structures that lie between the vertebrae. If the symptoms of lumbar osteochondrosis are not detected early, the condition can cause deformation of the body adjacent to the vertebrae, intervertebral joints. The blood vessels and nervous system are involved in the pathological process.
One of the most common forms of this disease is lumbar osteochondrosis, and symptoms are very similar in women and men. Many adults experience repeated discomfort in the lower back, sacrum, and legs caused by osteochondrosis and its complications. Of all the causes of loss of normal mobility, it is this disease that takes the top spot.
reason
One of the causes of this disorder is poor posture, but there are others:
- Osteochondrosis of the lumbosacral vertebra, with its symptoms and treatment causing a lot of inconvenience to patients, the most common cause is increased spinal pressure. This is why the disease is more common in those whose labor activities are related to manual labor and weight lifting.
- Another factor contributing to the disease is being overweight, which can increase the pressure on the spine.
- Absence of any load and lack of physical activity can worsen the nutrition of the disc tissue and slow down blood flow and metabolic processes in the spine. The muscular corset is significantly attenuated, creating a favorable background for the development of pathological changes.
- Incorrect body position, if the patient likes to sit with a hunched back, will cause uneven load on the intervertebral disc and vertebrae, and the intervertebral disc will deform and wear out quickly.
- The cause of lumbar osteochondrosis is often injury, and its symptoms bring a lot of inconvenience to the patient's life. They occur during exercise, exercising without proper preparation, improperly lifting weights, and being injured in a fall.
- Some experts believe that even at the genetic level, osteochondrosis is predetermined regardless of which particular sector degenerative changes are observed.
- The age of the patient also has a special effect: as the years pass, the spinal segments lose their mobility and elasticity and are therefore subject to destruction and deformation. Previously, osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine, with rather unpleasant symptoms, was considered a disease of the elderly, but today it occurs in young people between the ages of 25 and 30.
- Predisposing factors may be some lesions that accompany spondyloarthritis or changes in its structure and shape: ankylosing spondylitis, arthritis, scoliosis, disc instability.

In rare cases, osteochondrosis may develop due to:
- low temperature;
- pressure;
- malnutrition;
- Violation of work and rest regimes;
- harsh environmental conditions.
The first time you experience lower back discomfort, it is best to consult your doctor.
Classification by degree of osteochondrosis
The degree of osteochondrosis is used to systematically describe the clinical manifestations of the disease. This classification allows you to describe the symptoms of lumbar osteochondrosis and pinpoint exactly when a patient begins to suffer from pain:
- The first degree occurs when a disc ruptures, which is caused by sudden movement. It manifests in the form of a sharp sudden pain, a feeling of a person being hit in the spine, and the muscles tense reflexively.
- Secondary symptoms are similar to intervertebral herniation and instability of the spinal trunk. Physical activity exacerbates pain. Constantly alternating worsening and remission. In the case of osteochondrosis in the cervical spine, when a person stays in one position for a long time, the pain is exacerbated, and headaches, discomfort in the arms and shoulders, and fatigue in the lower extremities often occur.
- The third degree presents symptoms of a herniated disc: numbness in the extremities, changes in posture and gait, headache, and discomfort in the affected nerves. Symptoms may resemble kidney disease, gastrointestinal disease, and reproductive system disease.
- The fourth degree begins with anesthesia of the hernia, which may diminish, but the symptoms of spinal instability and twisting of the vertebrae persist. In addition, vertebral growth may occur, which often compresses the spinal nerves or blocks the spinal canal, allowing the back to press on the brain. If the hernia is surgically removed, this extent can be attributed to the consequences of the surgery.
Osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine, with its symptoms causing many inconveniences, is a rather unpleasant disease. It requires urgent complex treatment and constant monitoring by specialists.
pathological symptoms
Treatment for lumbar osteochondrosis may vary based on symptoms. This is because the disease affects the nervous system, which is why problems not related to the back often occur in different parts of the body.
In the early stages of the disease, pain may occur after strenuous physical exertion or holding one position for long periods of time, for example, a person often spends time sitting in front of a computer. Pain can become chronic as the disease progresses. If the pain syndrome does not manifest, it is replaced by discomfort that may interfere with normal life. The complexity of symptoms is as follows:
- lower back pain, usually radiating to the buttocks or legs;
- Muscle spasms in statistical positions for long periods of time;
- Persistent tension in the back muscles;
- Shooting in the back, which usually occurs after a person has been exposed to cold for an extended period of time;
- Sensory disturbances in the lower part of the patient's body;
- Numbness in the legs and frequent tingling in the fingers;
- cold legs;
- sweating dysfunction;
- Dry skin in the area where the pain occurs.

Symptoms of lumbar osteochondrosis may worsen if steps are not taken to cure the patient or if one of the predisposing factors becomes more intense. In this case, the pain syndrome is transmitted to the lower extremities. Instead of feeling the unpleasant discomfort caused by the disease, a person tries to find the most ideal position to relieve his condition.
diagnosis method
Initially, before starting a diagnosis, a doctor needs to collect a patient's medical records, examine him carefully, and assess his health. In addition, an instrument check method may be required.
A complete medical history will allow the physician to suggest the cause of the symptoms of lumbosacral osteochondrosis and assess the risk of its occurrence. Examination of the patient includes palpation of the painful area, percussion, and external examination of the skin. In some patients, doctors may use acupuncture to test for sensitivity.
Based on data collected by doctors, patients are advised to undergo additional instrumentation tests to confirm the diagnosis and determine how the spine and other organs are affected. Patients are advised to receive:
- radiography;
- nuclear magnetic resonance;
- Computed Tomography.
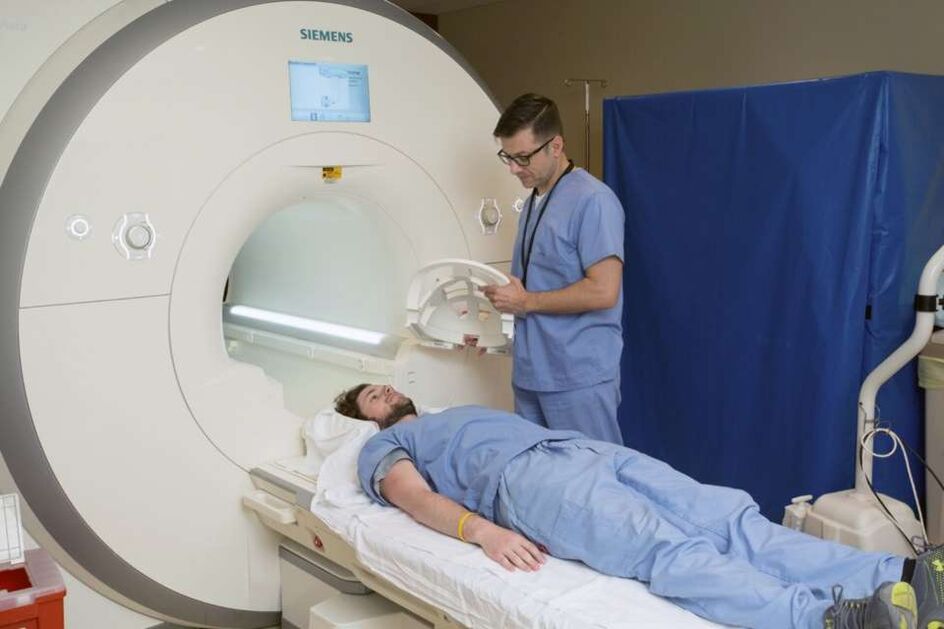
All of these diagnostic methods help identify certain features of disease development. MRI is considered to be the most informative of them all because other methods take pictures of the human body in only a few projections and do not allow a close look at the whole problem.
Treatment of lumbar osteochondrosis, whose symptoms begin to trouble a person, is chosen by the doctor. It is impossible to make a diagnosis and determine a course of treatment only through external examinations. It is important to conduct a comprehensive examination to prevent complications.
Treating lower back osteochondrosis
It is impossible to completely cure osteochondrosis. Good results can be achieved if the patient has 1st and 2nd degree disease. But anyway, lumbosacral osteochondrosis requires long-term treatment because the symptoms are unbearable, they are so intense and unpleasant. Treatment targets:
- Reduce the intensity of lumbosacral pain;
- Eliminate muscle tension that does not allow one to relax;
- Strengthen the muscles of the back, hips and lower extremities;
- normalizes blood flow and metabolic processes in the affected area;
- eliminate inflammatory processes;
- Restore normal range of motion in the waist and increase sensitivity in the legs;
- Improve the function of reproductive and excretory system organs.
Among medications, doctors prefer the following:
- Painkillers are definitely recommended. Analgesics help relieve pain, but they do not eliminate the cause of the disease.
- To eliminate swelling and radicular pain, use non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and, in severe cases, steroid drugs to eliminate symptoms of lumbar osteochondrosis in women and men. Their actions are designed to reduce and eliminate inflammation.
- For local anesthesia, a paravertebral block is used. The drug is administered along the waist. More commonly, they are recommended for patients with grade 3-4 disease.
- Muscle relaxants are recommended to eliminate spastic muscle contractions.
- Chondroprotective agents improve the metabolic processes of cartilage tissue, stimulate regeneration processes and significantly slow down its deformation.
- Vitamins belonging to the B group help improve cellular metabolism, reduce inflammation, and help remove excess fluid from the body.
- Diuretics help reduce swelling.
- Immunostimulants increase the activity of the immune system and improve the body's defenses.
- Methods to improve blood flow in areas affected by disease, administered by intravenous drip.
Complementary therapy
Your doctor may recommend additional physical therapy. Medication alone is not enough to treat lumbosacral osteochondrosis, the symptoms of which are painful for the patient. To eliminate pain and relieve muscle spasms, the following physical therapy procedures are recommended to improve metabolic processes:
- amplify the pulse;
- electrophoresis;
- Double power current;
- magnetic resonance therapy;
- magnetic therapy;
- Laser Treatment.
Therapeutic gymnastics will not be superfluous either, because with its help you can not only eliminate pain syndromes, but also strengthen and relax the muscles of the back. Physical exercise can be performed not only during pathological exacerbations, but also during recovery. Massage and reflexology are excellent.
Operation
Surgery may be recommended for some patients with stage 4 disease. This measure is used in cases where drug therapy does not achieve the expected results, severe neurological and motor disorders and the appearance of hernias. The herniated disc is surgically removed, followed by plastic surgery to reliably strengthen the displaced vertebrae.
folk remedies
The symptoms of lumbar osteochondrosis in men are not much different from those observed in women. Depending on the stage of the disease, treatment options are individually selected for each patient. In addition to traditional treatments, traditional medicines can also be recommended. The patient must coordinate all his actions with the doctor. These herbal products have achieved good results in complex treatments:
- To prepare a salve to improve circulation in the affected area, you will need to take five red peppers and 1/2 cup of kerosene and vegetable oil. After receiving a therapeutic infusion, they need to lubricate the painful area at night. Place a dry wool compress on top of the treatment area.
- Mix equal parts butter and hop cones, this composition is suitable for the lumbar area, when there is no strength to endure pain and discomfort.

Folk remedies have a good effect in the early treatment of lumbar osteochondrosis, and the pathological symptoms gradually disappear. Such recipes are best used immediately after the first signs of illness.
Consequences of disease
Symptoms of lumbar osteochondrosis in both men and women can cause significant inconvenience, with a person not being able to sit properly, sleeping poorly and often feeling unwell. Osteochondrosis can lead to serious complications in the form of inflammation of the sciatic nerve if measures are not taken in time at the first manifestations of the disease. The disease is characterized by severe pain in the lower back and legs, and even numbness in the extremities. To relieve pain, many patients walk, bending over to the healthy side, but this posture only aggravates the condition: the curvature of the spine increases and the disc destruction process accelerates.
The most dangerous complication can be considered vertebral instability. The intervertebral discs cannot cope with the function of immobilizing the vertebrae, and the lower back begins to slide off the sacrum under heavy load. This condition can lead to the destruction of internal organ systems. Women may experience inflammation of the uterus, adnexa, while men may experience potency issues.
Precaution
You can prevent this disease if you use:
- Eliminate heavy loads on the lower back;
- strengthen back muscles;
- maintain correct posture;
- Strengthen the spine through regular physical activity;
- Adhere to proper nutrition;
- regular rest;
- Treat low back pain promptly.

Only by timely medical treatment and comprehensive treatment, can there be a chance to prevent complications and return to the previous way of life.